Causes of Toothaches
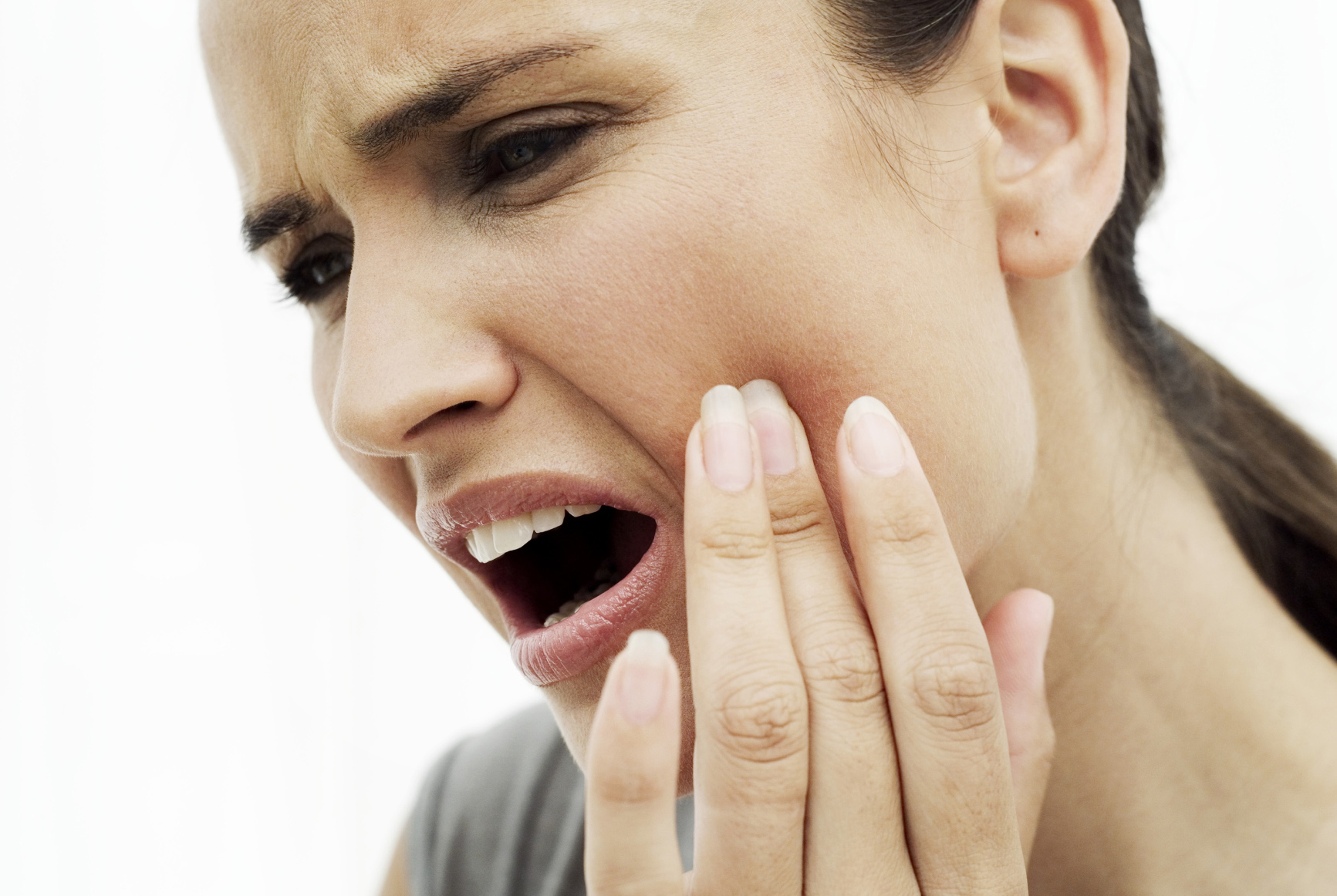
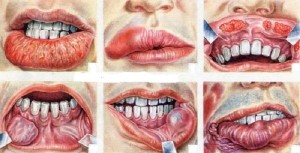
Toothaches have many causes, from gum disease to jaw clenching, but tooth root sensitivity can also cause a tooth to ache.
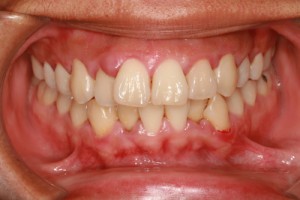
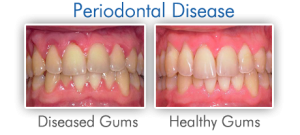
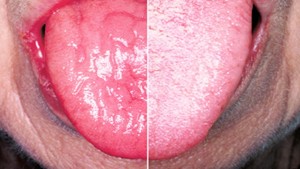
The tooth root includes the lower two-thirds of the tooth, and it is usually buried in the jawbone. But when gum disease develops, the bacteria that cause the disease can also dissolve the bone around the tooth root. The combination of dissolved bone and receding gums means that more of the tooth root is exposed. Without protection from healthy gums and healthy bone, the root often becomes sensitive to hot and cold and to sour foods.In some cases, the sensitivity is so severe that you may avoid very hot, cold or sour foods.
If the root exposure is not severe, try using a special toothpaste formulated for sensitive teeth that contains fluoride and other minerals. The extra fluoride and minerals will help to strengthen the exposed root and make it less sensitive.
The best way to manage root sensitivity and to prevent gum disease with a consistent oral health care program of twice-daily tooth brushing and daily flossing. Try a soft bristle toothbrush to avoid irritating your gums, which can increase the risk of root exposure and sensitivity