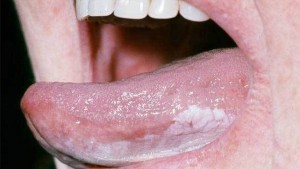
Leukoplakia is a reaction to a chronic irritation, like rough teeth, badly fitting dentures, smoking, and smokeless tobacco. It can show up as white patches or plaques in the mouth, is usually painless, and can’t be scraped off. Leukoplakia can also be a precancerous condition. Persistent patches or other changes in your mouth. Mild leukoplakia is usually harmless and generally goes away on its own. More serious cases may be linked to oral cancer.
Symptoms of Leukoplakia:-
This condition is marked by unusual looking patches inside the mouth. These patches can vary in appearance. Generally, patches resulting from leukoplakia have the following features:
- white or grey color
- thick, hard, and raised surface
- hairy (hairy leukoplakia only)
Rarely, the patches have red spots. Redness may be a sign of cancer. Leukoplakia most often occurs on the tongue. However, cheeks and gums are also vulnerable. The patches may take several weeks to develop, but they are rarely painful. Causes:-Smoking is the most common cause. Chewing tobacco can also cause leukoplakia. Biting the cheek, rough uneven teeth and dentures (especially if improperly fitted).
What Causes Leukoplakia?
- Irritation from rough teeth, fillings, or crowns, or ill-fitting dentures that rub against your cheek or gum
- Chronic smoking, pipe smoking, or other tobacco use
- Sun exposure to the lips
- Oral cancer (although rare)
- HIV or AIDS
What Are the Symptoms of Leukoplakia?
The presence of white or gray colored patches on your tongue, gums, roof of your mouth, or the inside of the cheeks of your mouth may be a sign of leukoplakia. The patch may have developed slowly over weeks to months and be thick, slightly raised, and may eventually take on a hardened and rough texture. It usually is painless, but may be sensitive to touch, heat, spicy foods, or other irritation.
How Is Leukoplakia Diagnosed?
Your dentist may suspect leukoplakia upon examination; however, a biopsy will likely be taken to rule out other causes, such as oral cancer. During the biopsy, a small piece of tissue from the lesion will be removed to be examined in a lab. A numbing agent will be used so that you will not feel any pain.
Treatment for Leukoplakia?
Treatment for leukoplakia, if needed, involves removing the source of irritation.
For example, if leukoplakia is caused by a rough tooth or an irregular surface on a denture or a filling, the tooth will be smoothed and dental appliances repaired.
If leukoplakia is caused by smoking, you will be asked to minimize or stop smoking or using other tobacco products.