Methamphetamine (meth) is a dangerously addictive drug that can have severe health consequences, including stroke and permanent brain damage. It’s also devastating to your dental health.
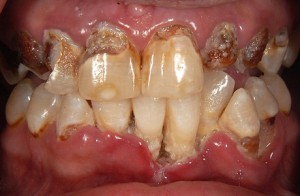
“Meth mouth” is characterized by severe tooth decay and gum disease, which often causes teeth to break or fall out. An examination of the mouths of 571 methamphetamine users showed:
- 96% had cavities
- 58% had untreated tooth decay
- 31% had six or more missing teeth
The teeth of people addicted to methamphetamines are characterized by being blackened, stained, rotting, crumbling and falling apart. Often, the teeth cannot be salvaged and must be removed. The extensive tooth decay is likely caused by a combination of drug-induced psychological and physiological changes resulting in dry mouth and long periods of poor oral hygiene. Methamphetamine itself is also acidic.
Meth – also known as speed, ice, glass and crystal – can be smoked, snorted, injected or taken in pill form and is highly addictive. The high (which causes the brain to feel intense pleasure) can last up to 12 hours. This can lead to long periods of poor dental hygiene. While high, users often crave high-calorie, carbonated, sugary beverages. In addition, they may grind or clench their teeth, all of which can harm teeth.
In the short term, meth can cause shortness of breath, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, insomnia, hyper activity, decreased appetite, tremors and trouble breathing. Over time, meth can cause irregular heartbeats, high blood pressure, stroke, violent behavior, anxiety, confusion, paranoia, hallucinations and delusions. It can also negatively affect ability to learn long-term.
I