Tongue thrust, also known as reverse swallow or deviate swallow, is a condition in which the tongue is pressed up against the teeth or between them while gulping. In many cases, this condition leads to the movement of the tongue incorrectly to the sides, instead of moving forward to the teeth. This improper positioning of the tongue can occur even as the tongue is at rest, and in this case, it will lie too far forward.
Types of Tongue Thrust
Tongue thrust is an orofacial myofunctional disorder (OMD), having many different types.
- Unilateral thrust when the tongue pushes unilaterally to the sides between the back teeth during swallowing
- Anterior thrust refers to the case when the upper incisors are extremely protruded and lower lip is pulled in by the lower lip.
- Bilateral thrust, when the tongue pushes between the back teeth on both sides during swallowing. Large tongue can also be noted
Tongue thrust in babies
In babies who are breastfed or bottle-fed, tongue thrust is normal. As the child gets older, their swallowing and speaking pattern should evolve.
However, some types of bottle nipples — and prolonged use of a bottle — can lead to an abnormal tongue thrust that lasts past the infant stage and into early childhood.
There are several other potential causes for tongue thrust that begin in infancy. Some of these include:
- Long-term sucking habits that influence the tongue’s movement, like sucking of the thumb, fingers, or tongue
- Allergies accompanied by chronically swollen tonsils or adenoids
- Tongue-tie, where the band of tissue beneath the tongue is tight or short
- A swallowing pattern known as reverse swallow
Tongue thrust has a number of telltale signs that manifest in children who have developed the pattern. These can include:
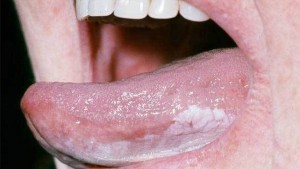
- Tongue is visible between the teeth. The tip of the tongue sticks out between the teeth, whether the child is resting, swallowing, or speaking.
- Mouth breathing.
- Inability to close the lips completely. This could be due to a structural abnormality or habit.
- Open bite. This occurs when the front teeth don’t meet when the teeth are closed.
- Slow, fast, or messy eating.
- Speech impediment. Lisping of s and z sounds is common.
Treatment of Tongue thurst
Tongue thrust often corrects with time or at the age of 8-9 years. Self-correction is due to musculature Balance during swelling.
- Orthodontic treatment can be carried out.
- Speech therapy is indicated.
- If an associated habit is present like thumb sucking than it must be treated first.
- Training the tongue for correct swallow & posture.
- Use of appliances to correct position of tongue.
- Correction of Malocclusion.


![Mother with her cute little daughter visiting a dentist for a checkup. [url=http://www.istockphoto.com/search/lightbox/9786662][img]http://dl.dropbox.com/u/40117171/medicine.jpg[/img][/url] [url=http://www.istockphoto.com/search/lightbox/9786738][img]http://dl.dropbox.com/u/40117171/group.jpg[/img][/url] [url=http://www.istockphoto.com/search/lightbox/9786778][img]http://dl.dropbox.com/u/40117171/family.jpg[/img][/url]](http://www.thedentalarcade.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/child-300x200.jpg)