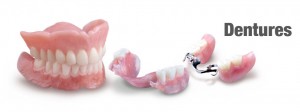
DENTURES
Dentures are removable appliances that can replace missing teeth and help restore your smile. If you’ve lost all of your natural teeth, whether from gum disease, tooth decay or injury, replacing missing teeth will benefit your appearance and your health. When you lose all of your teeth, facial muscles can sag, making you look older. Dentures can help fill out the appearance of your face and profile. They can be made to closely resemble your natural teeth so that your appearance does not change much. New dentures may feel awkward for a few weeks until you become accustomed to them. The dentures may feel loose while the muscles of your cheek and tongue learn to keep them in place. It is not unusual to experience minor irritation or soreness. You may find that saliva flow temporarily increases. As your mouth becomes accustomed to the dentures, these problems should go away.
Ceramic Braces
They are made of translucent (clear) material. They are most popular with adult patients, due to their cosmetic appeal.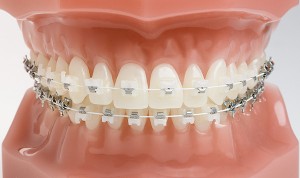
Ceramic braces are the same size and shape as metal braces, except that the brackets are tooth colored to help make a fixed brace look less noticeable.This type of brace straightens teeth without compromising the way you look during your treatment. For this reason ceramic braces are popular with adults. Ceramic fixed braces are strong, lightweight, comfortable and fixed to the front of your teeth. You’ll hardly notice they are there.
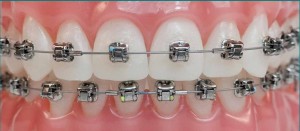
ORTHODONTIC TREATMENT WITH METAL BRACES
Orthodontic treatment is the science where the position and shape of the teeth is altered so as to make the teeth functionally and visibly more appropriate.
This type of treatment involves putting of small metallic brackets on the inner or outer surface of the teeth and then putting a wire through the brackets. this wire is held on with the help of little rubber bands. you can choose the color of the little bands and experiment with a variety of colors ranging from the traditional transparent ones or ones of neon colors.
The wire is then tightened approximately every month until the teeth reach the desired position.
The treatment once started cannot be stopped midway if the desired results want to be achieved.
PROS OF METAL BRACES
They are highly effective in bringing our teeth in alignment.
- need to be tightened only once a month
- most cost effective method for straightening teeth.
- can make even minor changes in later stages
- They are visually unaesthetic.
- if not cleaned properly they tend to accumulate food and debris.
- you need to keep the mouth absolutely clean at all timed.
- sometimes the brackets come off in case of trauma to the bracket or teeth in that case a dentist needs to be visited to replace the bracket.
- the wire needs to be tightened every month so you need to be present . the process cannot be too early or too late to get the desired results.
Paramolar
A supernumerary tooth lying among, lingual to, or buccal to the maxillary or mandibular molars. Paramolar is a developmental anomaly and has been argued to arise from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Supernumerary teeth can be found in almost any region of the dental arch. They are most frequently located in the maxilla. The crowns of supernumerary teeth may show either a normal appearance or different atypical shapes and their roots may be completely or incompletely developed.
Enamel pearl
Enamel pearl is a condition of teeth where enamel is found on locations where enamel is not supposed to be, such as on a root surface. They are found usually in the area between roots, which is called a furcation, of molars. Enamel pearls are not common in teeth with a single root. The most common location of enamel pearl is the furcation areas of the maxillary and mandibular third molar roots.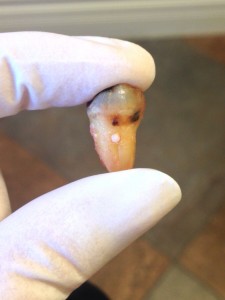
Scaling and Polishing
What is it?
A scale and polish cleans your teeth very thoroughly.
Scaling removes the hard tartar which forms on your teeth like scale inside a kettle. You can’t remove it just by brushing your teeth. Scaling also removes trapped food and plaque containing millions of germs, which can cause tooth decay and gum disease. Stains from coffee, tea, cigarettes or red wine are also cleaned away when your dentist polishes your teeth.
A dental hygienist is specially trained and will scale your teeth. If you clean your teeth very thoroughly anyway, your scale and polish will take less time.
What happens?
There are two ways to scale teeth.
- Hand scalers – These come in different sizes and shapes, to reach different parts of your teeth. This is why you will see the hygienist changing instruments quite often.
- Electric scalers – These use very fast vibration with water. The water is sucked out of your mouth. A hand scaler is used to check whether the teeth are completely clean.
For polishing, your hygienist will use a rotating brush or rubber polisher with toothpaste.
Scaling cleans above and below the gums. If you have gum disease, scaling needs to be deeper, around the roots of the teeth.
This is called ‘root planing’. Your hygienist may give you a local anaesthetic to make it more comfortable.
Your dental hygienist will tell you about the best way to clean your teeth and gums thoroughly at home.
Good Morning everyone,
According to a prevalent myth in connection with Danteshwari, due to an insult committed by her father Prajapati Daksha towards her consort Lord Shiva during a Yaggya, Goddess Sati got frustrated and committed self-immolation in the fire pit of yaggya. Lord Vishnu cut the dead body of Goddess Sati into pieces with his Sudarshan to make Lord Shiva free from the grief caused by the death of Sati. Parts of the dead body of Goddess Sati were scattered to fifty-two different places, which were consecrated as Shakti Pithas by different names. It is believed that a tooth of Sati had fallen here and Danteshwari Shaktipith was established. 
Fluoride
Fluoride is a mineral that occurs naturally in many foods and water. Every day, minerals are added to and lost from a tooth’s enamel layer through two processes, demineralization and remineralization. Minerals are lost (demineralization) from a tooth’s enamel layer when acids — formed from plaque bacteria and sugars in the mouth — attack the enamel. Minerals such as fluoride, calcium, and phosphate are redeposited (remineralization) to the enamel layer from the foods and waters consumed. Too much demineralization without enough remineralization to repair the enamel layer leads to tooth decay. 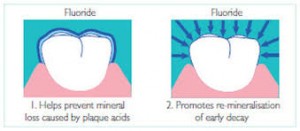 Fluoride helps prevent tooth decay by making the tooth more resistant to acid attacks from plaque bacteria and sugars in the mouth. It also reverses early decay. In children under 6 years of age, fluoride becomes incorporated into the development of permanent teeth, making it difficult for acids to demineralize the teeth. Fluoride also helps speed remineralization as well as disrupts acid production in already erupted teeth of both children and adults.
Fluoride helps prevent tooth decay by making the tooth more resistant to acid attacks from plaque bacteria and sugars in the mouth. It also reverses early decay. In children under 6 years of age, fluoride becomes incorporated into the development of permanent teeth, making it difficult for acids to demineralize the teeth. Fluoride also helps speed remineralization as well as disrupts acid production in already erupted teeth of both children and adults.
Torus mandibularis
Torus mandibularis is a benign peculiarity wherein there is a bony outgrowth on the palate. It is a normal bump on the roof of the mouth. It is one of the most common exostosis involving the oral cavity. It is not cancerous, nor it is painful or sore .It comes in different shapes: nodular, spindle-like, lobular, or irregular. It is hard upon palpation and radiography shows opacity on this area due to the bone’s density. Since it is normal, there is no symptom associated with it. It is believed that mandibular tori are caused by several factors. They are more common in early adult life and are associated with bruxism. The size of the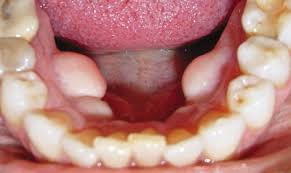 tori may fluctuate throughout life, and in some cases the tori can be large enough to touch each other in the midline of mouth. Consequently, it is believed that mandibular tori are the result of local stresses and not solely on geneticinfluences.
tori may fluctuate throughout life, and in some cases the tori can be large enough to touch each other in the midline of mouth. Consequently, it is believed that mandibular tori are the result of local stresses and not solely on geneticinfluences.