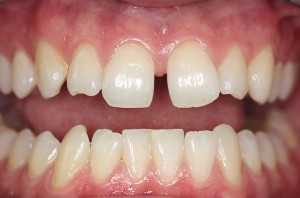
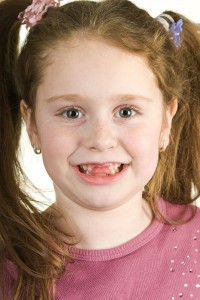
Whether you love it or hate it, that space between your teeth has a name. A diastema is a gap between two teeth. Many celebrities are famous for their midline diastema, or space between their two upper front teeth.Diastemas are extremely common, especially among children. A diastema is a natural part of a child’s development and may correct on its own. In fact, up to 97 percent of children have diastemas, and that number significantly decreases as children grow and these spaces close up naturally. If a diastema remains after the eruption of adult teeth, it will become permanent and can only be corrected with professional diastema treatment.
Diastema Causes
There are several reasons that permanent diastemas form. A diastema is often the result of a discrepancy between the size of the jaws and the size of the teeth. Crooked teeth usually come from overcrowding, where the teeth are too big for the jaw. The opposite is true for a diastema — teeth that are too small for the jaw may have gaps between them. Diastemas may also be caused by missing teeth, undersized teeth or bad oral habits, such as excessive thumb-sucking.A midline diastema can also be caused by a large labial frenum. Frenum is the tissue that connects your lips and gum.
Diastema Closure :- Diastemas usually cause no complications to your dental health, but many people choose diastema closure for cosmetic purposes. There are several types of diastema treatment available today.
Dental Braces — Most diastemas require a full set of dental braces and retainer therapy, as moving one tooth can affect the placement of the rest.