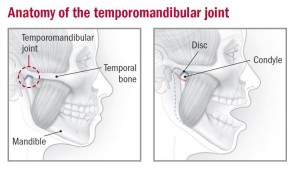
Overview
Temporomandibular joint and muscle disorders, commonly called “TMJ,” are a group of conditions that cause pain and dysfunction in the jaw joint and muscles that control jaw movement.
Some estimates suggest that TMJ disorders affect over 10 million Americans. These conditions appear to be more common in women than men.
Causes
Trauma to the jaw or temporomandibular joint plays a role in some TMJ disorders, but in most cases, the exact cause of the condition is not clear. For many people, symptoms seem to start without obvious reason.
Symptoms
A variety of symptoms may be linked to TMJ disorders. The most common symptom is pain in the chewing muscles and/or jaw joint. Other symptoms include:
- radiating pain in the face, jaw, or neck,
- jaw muscle stiffness,
- limited movement or locking of the jaw,
- painful clicking, popping or grating in the jaw joint when opening or closing the mouth,
- a change in the way the upper and lower teeth fit together.
Diagnosis
There is no widely accepted, standard test now available to correctly diagnose TMJ disorders. Your doctor will note your symptoms, take a detailed medical history, and examine problem areas, including the head, neck, face, and jaw for tenderness, clicking, popping, or difficulty with movement. The doctor might also suggest imaging studies such as an x-ray.
Treatment
Conservative Treatments
Because the most common jaw joint and muscle problems are temporary and do not get worse, simple treatment may be all that is necessary to relieve discomfort. Short term use of over-the-counter pain medicines or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen; the use of a stabilization splint, or bite guard, that fits over upper or lower teeth may provide relief.
Irreversible Treatments
Surgical treatments are controversial, often irreversible, and should be avoided where possible. There have been no long-term clinical trials to study the safety and effectiveness of surgical treatments for TMJ disorders.
Self-care practices that may help ease symptoms of TMJ:
- eating soft foods,
- applying an ice pack,
- avoiding extreme jaw movements like wide yawning, loud singing, and gum chewing,
- learning techniques to relax and reduce stress,
- practicing gentle jaw stretching and relaxing exercises that may help increase jaw movement. Your health care provider or a physical therapist can recommend exercise